surveys
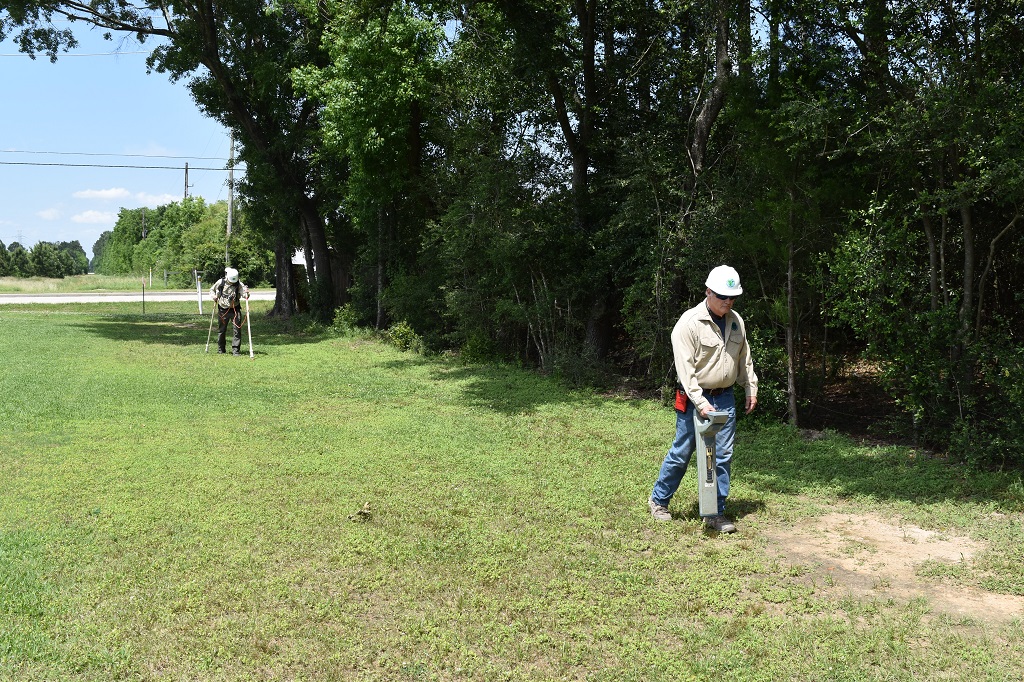

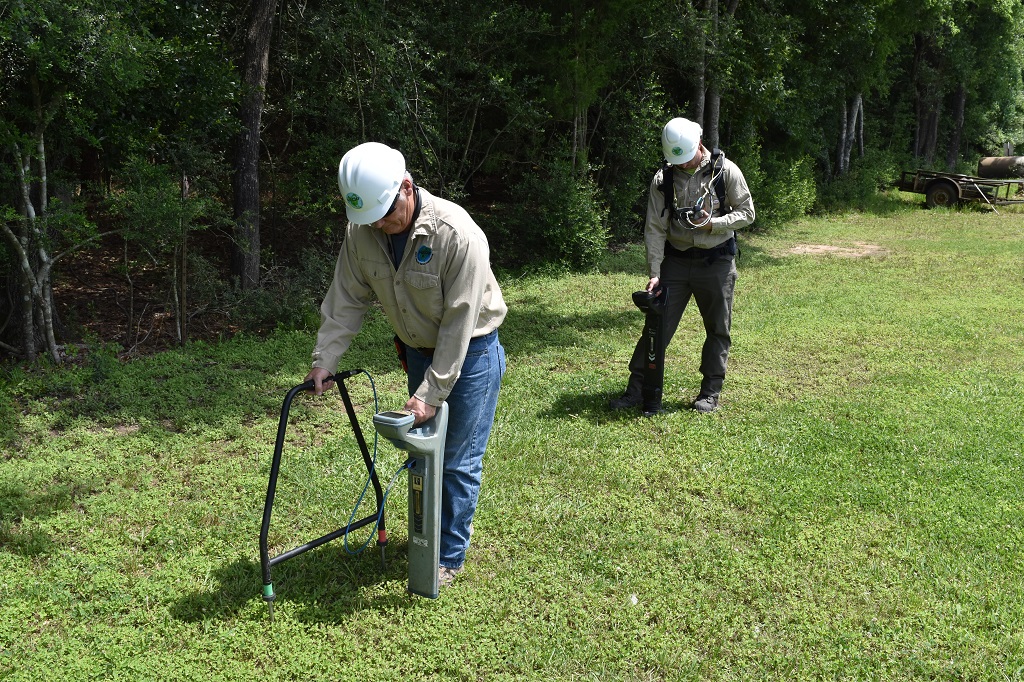
Close Interval Survey
Close Interval Survey
CIS (Close Interval Survey) is the process of identifying possible corrosion problems in modern product pipelines. For this purpose, NASCORP uses a data logger equipped with a magnetic-read wire counter for use in measuring distance as well as corresponding sub-meter GPS collection. Magnetic wire counters offer a high degree of accuracy which will result in a better representation of distance in your field plots. Underground structures are protected from corrosion by using method called cathodic protection which uses either an impressed DC current (rectifiers) or a sacrificial (anodes) and equipped with permanent test stations where wire leads are attached to the pipeline to measure the pipe-to-soil potential. This potential should be adequately cathodic to ensure proper corrosion protection but not excessively cathodic which can cause hydrogen disbondment the coating.
There are several types of (CIS) Close Interval Surveys:
- ON SURVEY – this survey collects data between established test stations (usually at 2.5 to 5 foot intervals). As with all types of close interval surveys, the “ON” pipe-to-soil readings are obtained using a traveling reference electrode coupled with light gauge coated wire, a data recorder and sub-meter GPS equipment. The operator provides a continuous profile of the pipe-to-soil potentials as well as any right-of way features of note on the structure being surveyed.
- ON/OFF SURVEY (Interrupted) – This survey requires the DC current on the structure be interrupted for a specific time sequence such as 4 seconds on and 1 second off to minimize depolarization. The current is interrupted to remove the IR from the line to obtain the polarized or instant off potential. The polarized or instant off pipe-to-soil potential must be more negative than -850mV in order to meet D.O.T. specifications.
- DEPOLE, STATIC or NATIVE SURVEY – This survey is used when the pipe in question is having trouble meeting the off criterion of -850mV. The cathodic protection system protecting the pipeline is completely turned off to allow the pipeline to depolarize to its native or depolarized potential. If the difference between the instant off potential and the depolarized potential of 100mV or greater, the pipe is considered protected per D.O.T. requirements.
The on/off survey is especially useful in identifying sources of influence. When used in conjunction with ACVG or DCVG surveys, we can provide clients with a more thorough assessment of a pipe’s coating condition.
North American Survey uses:
- Three member crews with one or two vehicles.
- Experienced, certified crew leaders, data collectors and pipe locators.
- Satellite synchronous interrupters (AC or DC) and data loggers.
- Hip pack or backpack wire dispensing unit with either magnetic switch chainer.
- An American Innovations Allegro based handheld data logger.
- 34 AWG gauge copper wire with lacquer insulation.
- Daily reporting

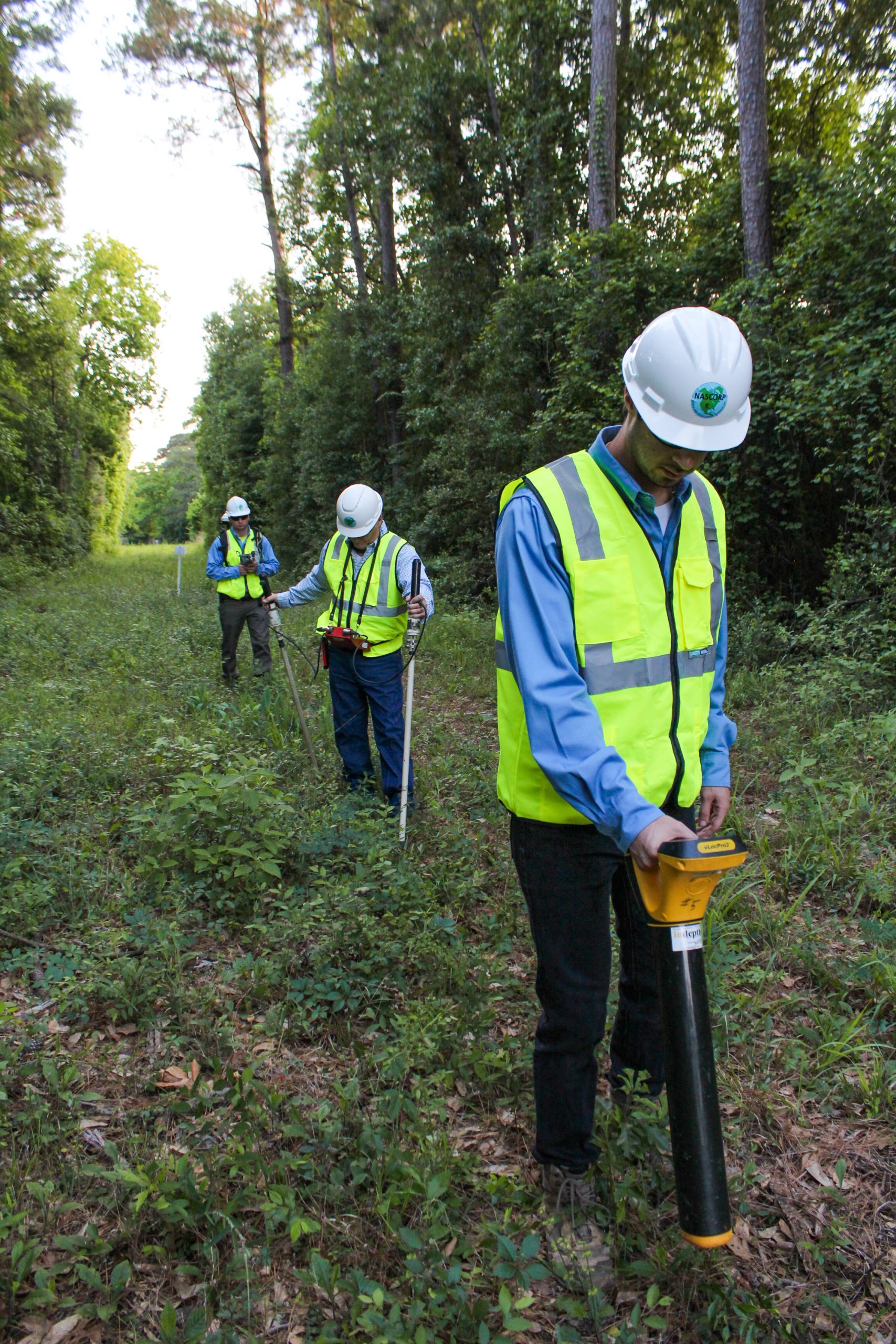
ACVG
ACVG (Alternating Current Voltage Gradient)
ACVG surveys are used as an indirect inspection tool as part of the ECDA program on a line. Through use of the PCM (Pipe Current Mapper) and A-Frame unit & receiver, we can locate coating anomalies with high accuracy. This process is very similar to the DCVG (Direct Current Voltage Gradient) process except ACVG evaluates the coatings on pipelines by using a signal generator for alternating current. This survey is especially useful on newer, well-coated lines due to the high-level of sensitivity. It’s also advantageous in locations with congested piping such as multi-line corridors, pump stations, chemical plants as you can control the location of the signal generator and size the indication more accurately. Anomalies are classified as 3 or 4 arrow indications with severity determined by corresponding decibel readings. The higher the decibel indication, once converted to a 1-amp scale, the more severe the anomaly. Accuracy also depends on pipe depth and soil conditions.

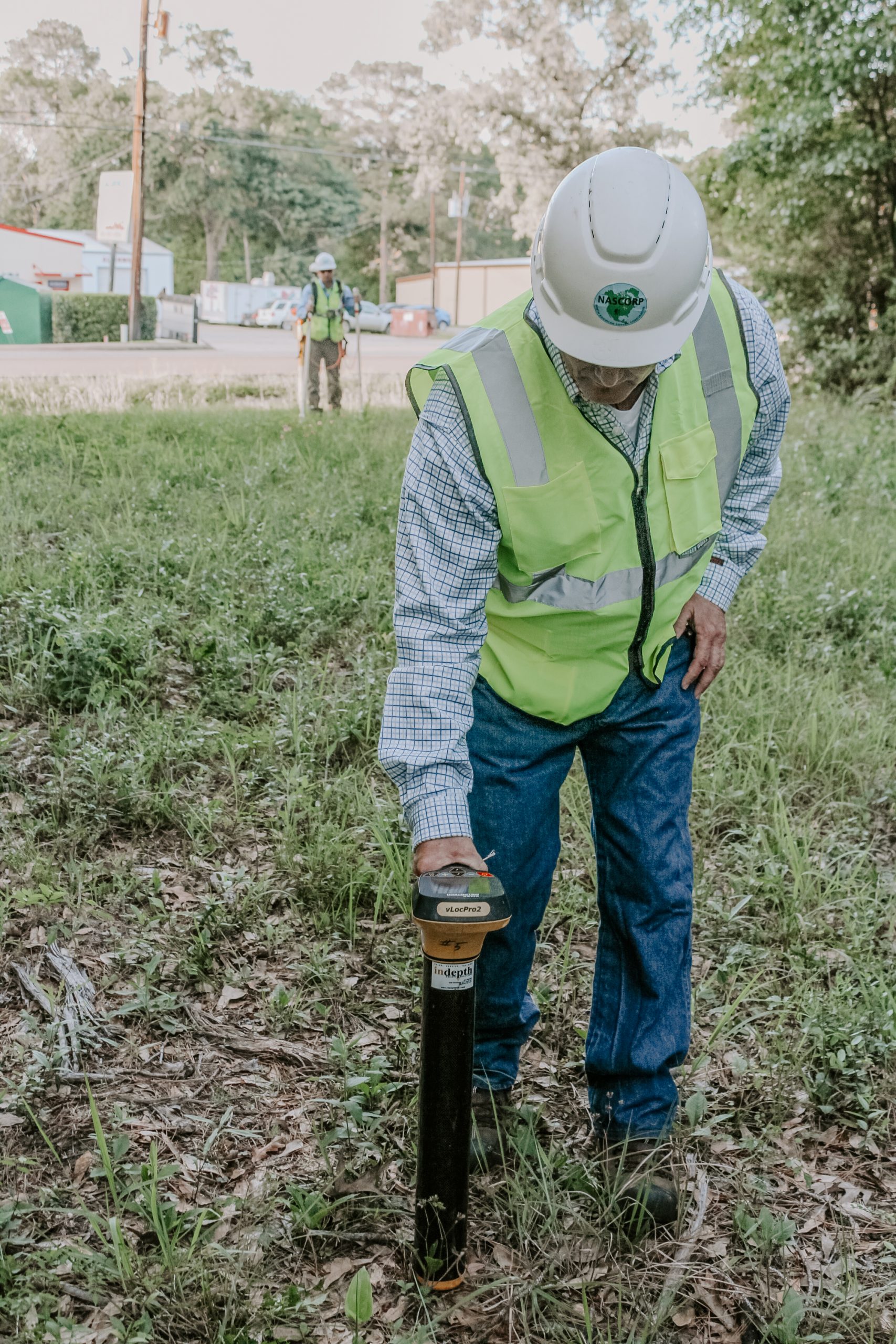
DCVG
DCVG (Direct Current Voltage Gradient)
DCVG is a survey technique used for locating and sizing of pipeline coating defects. Basically, this method measures voltage gradients on pipelines with impressed DC current. It relies on a pulsed-ON reading to determine current direction. Accuracy of location and severity are very precise. This method uses either an analog or digital meter coupled with sub-meter GPS to provide improved accuracy and reliability. As with ACVG, the accuracy depends on the soil conditions. Coupled with close interval survey, this method is highly effective for ECDA.

Depth of Cover
Depth of Cover
A depth-of-cover survey allows the client to decide as to whether sufficient cover between the top of the pipeline and the ground level is present to meet local, state, and federal regulations. Proper cover protects the pipeline from third-party human activities and environmental scour. Regulations may vary from state to state on the requirements for the depth of a pipeline and how often a depth-of-cover survey must be conducted. Depth-of-cover surveys are typically conducted periodically per operator specifications and are often coupled with other survey types such as close interval or ACVG/DCVG. In areas of cultivation or higher than normal erosion, a survey may need to be conducted every few years.

Soil Resistivity
Soil Resistivity
Soil resistivity is a measure of how much the soil resists the flow of electricity. It is a critical factor in design of systems which rely on current passing through the Earth’s surface. Soil Resistivity testing measures the resistance of soil. Soil resistivity testing generally requires a combination of the following components:
- Soil resistivity test instrument
- Metal pins
- Wiring
- Probe with two isolated electrodes
- AC or DC current source
- Ammeter and voltmeter
- Soil box
Equipment necessary to perform a soil resistivity testing depends on the soil resistivity method selected for the survey. Typical methods of measuring soil resistivity are as follows:
- Wenner 4-Pin
- Single Probe
- Soil Box

Annual
Annual Test Point Surveys
An Annual Test Point survey is a mandated procedure required by the D.O.T. Pipe-to-soil readings are collected at each test point and above ground structure associated with a given system or structure. This information is vital in the assessment of cathodic protection status for structures such as pipelines, casings, tank bottoms, etc. This survey type can be conducted singularly or coupled with other survey methods such as close interval surveys. North American Survey Corp conducts a thorough survey with data collection readings such as pipe-to-soil, structure-to-soil, AC, foreign line pipe-to-soil, etc. each with corresponding sub-meter GPS and is formatted to meet the operator’s requirements in a timely fashion.

Bi-Monthly
Bi-Monthly Rectifier Readings & Assessment
Bi-monthly rectifier surveys are mandated by the D.O.T. for regular assessment of the proper functionality of the Operator’s cathodic protection units. North American Survey can provide thorough documentation of all settings, voltage and current output and physical unit assessment as well as local structure-to-soil readings in the immediate area with corresponding sub-meter GPS to meet the Operators requirements coupled with general housekeeping and minor repairs as needed.

Current Attenuation
AC Current Attenuation
ACCA surveys are typically conducted to obtain a coating assessment for a large section of pipeline. When conducting a survey, the current attenuation readings are generally recorded at intervals of 100 feet or per client specifications. Extended intervals allow for faster surveys of larger sections of pipeline.
The purpose of conducting ACCA surveys is to locate possible coating deficiencies, or holidays. Unlike other survey methods which are used to pinpoint coating defects, ACCA surveys are typically used to identify more general areas which may potentially have coating deficiencies. When a fault is encountered, the current quickly drops. A fault may be the result of coating damage. Loss of current is typically proportional to the amount of CP current being used at the fault.
While the accuracy of ACCA surveys is considered reliable over longer distances, they may not be as accurate as other methods over shorter distances. Industry practices usually dictate if an area of concern is indicated through an ACCA survey, another external direct assessment survey method such as ACVG or DCVG are used to pinpoint and confirm the ACCA results.

Cell to Cell
Cell to Cell
Cell to Cell surveys are a polarity survey used most often on very poorly coated or bare metal distribution lines. It involves the use of a high resolution voltmeter, two half cells, and a log sheet or a data recorder with sum meter accuracy. The half cells are placed 10 ft apart with the negative lead in the forward position over and parallel to the pipe. While moving the electrodes forward in 10 foot increments, recordings are made of the polarity and the mv potential. When the polarity changes from positive to negative, the forward or negative electrode is then walked backward until a positive reading is achieved. The hot spot is located at that point and is recorded.
Global Positioning
Global Positioning
North American Survey Corp uses Trimble, Satloc and Hemisphere GPS systems with differential correction collection units with real-time sub-meter GPS and attribute data anywhere in North America.
GPS surveying options include:
- Real time display ERDAS – DIG
- AutoCAD – DXF
- ARC/Info – GEN/attribute
- GeoLink – GLM
Information output options
- Latitude, longitude, altitude
- Time, date
- Attribute types
- Entity number
- Units of measure
- Degrees
- International feet
- US survey feet
- Radians
- Meters
- Miles
- Nautical miles
- Kilometers
Datum Selections
- WGS 84, WGS 72, NAD 83, NAD 27
- 12 additional international datums for data collector
- 99 additional for data manager
consulting and data analysis

Expertise at Your Fingertips
Looking for a reliable team to assist you with consulting and data analysis? Look no further! NASCORP’s combination of cathodic protection expertise and pipeline surveying experience provides pipeline operators and corrosion technicians with a valuable resource in completing pipeline integrity management initiatives and handling increased regulatory standards. We look forward to helping you examine your options and exceed your goals.
NCCER Assessment Facility

Accredited Assessment Center &
Accredited Training Sponsor
NCCER assists construction organizations and companies in implementing strong workforce development programs while helping individuals get the training and assessments they need to build successful careers in the construction industry.
NASCORP is an official NCCER training and assessment facility, and it would be our pleasure to help you get set up for continued success. Please fill out the Contact Form below and let us know what we can do for you.
![]()
![]()
